The brain is one of the body’s most vital organs and is responsible for what we do, say, and think. Ultimately, any trauma to this organ can lead to detrimental effects, some of which can lead to permanent cognitive or physical impairment or even death.
A traumatic brain injury (TBI) occurs when a violent blow, hit, bump, or jolt to the head disrupts the normal functioning of the brain. Every person is at risk of sustaining a TBI, especially young children older adults. Here are some statistics to put the entirety of this problem in perspective:
- About 2.8 million Americans sustain traumatic brain injuries each year. That comes out to about a TBI sustained every 21 seconds in the U.S.
- More than 56,000 people die each year because of TBI.
- Traumatic brain injury disables six times more people each year than spinal cord injuries, multiple sclerosis, HIV/AIDS, and breast cancer combined.
- About 5.3 million Americans currently live with long-term or lifelong disabilities that interfere with their daily activities.
Common causes of brain injuries
The severity of a brain injury will depend on several factors, including the nature of the accident and the force of the blow to the head. According to the Mayo Clinic, the following events are the most common causes of traumatic brain injury:
- Falls. Falls are the leading cause of TBI, especially in older adults and young children. These often occur from ladders, stairs, second-story windows, or on wet floors.
- Vehicle Collisions. Car accidents, motorcycle accidents, pedestrian accidents, or truck accidents are the leading cause of TBI-related death in youth adults.
- Violence. This includes gunshot wounds, assaults, and child abuse.
- Sports Injuries. The most common sports that result in TBI include boxing, football, soccer, hockey, baseball/softball, lacrosse, skateboarding, and other high-impact sports.
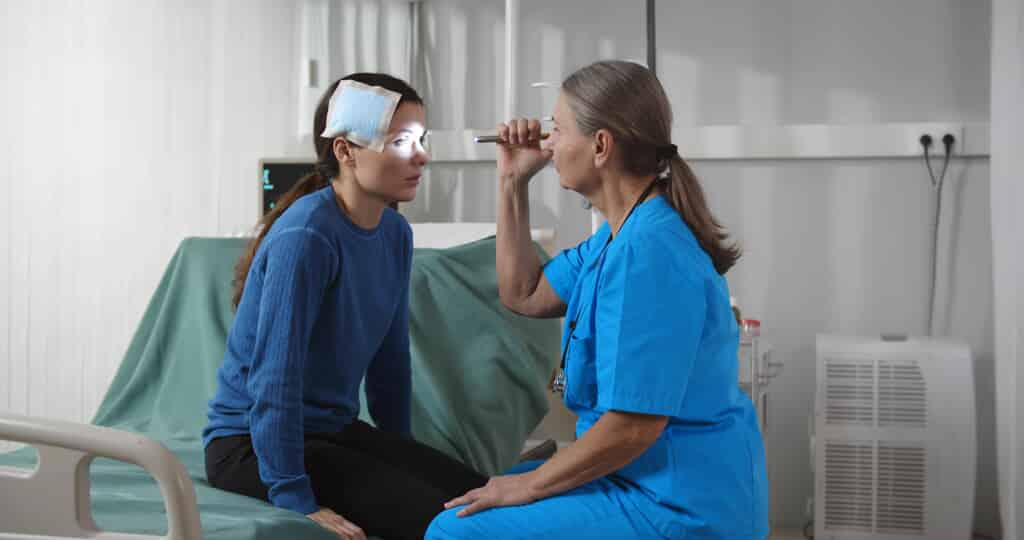
Diagnosing a brain injury
Traumatic brain injuries are known as a “silent epidemic” because they often don’t show immediate symptoms; in fact, some symptoms don’t manifest until days or weeks after the accident. Below are some of the symptoms that you should always keep your eyes out for in the time following a head injury:
Mild TBI
- Headaches
- Ringing in the ears
- Trouble remembering
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Blurry vision
- Confusion or brain fog
- Forgetfulness
- Concentration problems
- Sleep disturbances
Moderate/Severe TBI
- Loss of consciousness for several minutes to hours after the accident
- Persistent headaches
- Convulsions or seizures
- Dilation of one or both pupils
- Clear fluids draining from the ears or nose
- Weakness or numbness in the fingers and toes
- Profound confusion
- Agitation or combativeness
- Slurred speech
- Persistent anxiety and depression symptoms
- Sleep disorders
Long-term effects and treatments available
Oftentimes, mild traumatic brain injuries (concussions) will heal on their own within a few weeks. A doctor may recommend that the person stop all daily activities, including work or sports, for a period of time in order to help the injury heal and to reduce the risk of worsening the condition.
About 10-15% of concussion patients may develop post-concussion syndrome, which is defined as the presence of persistent symptoms that last longer than a month. Additionally, recurrent concussions can drastically increase the risk of a person developing permanent brain damage.
A person who sustains a moderate or severe TBI may experience a variety of deficits or long-term issues that may affect:
- Motor Function. This may include extremity weakness, impaired coordination and balance, or paralysis.
- Cognitive Function. This may include attention and memory problems, impaired reasoning, and impaired empathy.
- Sensation. Hearing, vision, perception, and physical touch may be impaired.
- Behavior. Behavioral deficits may lead to depression, anxiety, aggression, and personality changes.
In many instances, these brain injury survivors will require various types of rehabilitation or therapy in order to help them relearn certain skills and improve their ability to live independently. Some types of rehabilitation therapy that may help the individual include:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech and language therapy
- Psychiatric therapy
We are here to help your family
We understand that a traumatic brain injury can be absolutely devastating and affect your quality of life for years to come. You shouldn’t be left to deal with it on your own, especially if you did nothing wrong.
At Huffman & Huffman, our Newport News traumatic brain injury attorneys are dedicated to protecting the rights of those injured across Virginia since 1973. Whatever the situation of your accident, we will fight hard on your behalf to ensure you receive the compensation and justice you deserve.
Contact our firm at (757) 599-6050 to schedule your free, no-obligation consultation.
 Text Us
Text Us  Call Us
Call Us